SALES! The success – determining factor of every e-commerce business. For the same reason, converting a visitor to a lead and then to a paying customer is the holy quest every SEO and marketing strategist is after. This might seem like a challenging task. But thanks to e-commerce funnels or conversion funnels, one of the brilliant strategies for boosting e-commerce sales can make it possible. Our SEO strategy team in Perth help you understand how to use e-commerce funnels to boost sales.
What are e-commerce funnels?
An e-commerce funnel or conversion funnel is a way to understand the route a customer takes from being aware of your brand to the point of purchase. Depending on the type of business and service you provide, the funnel might be different. However, the fundamentals remain the same.
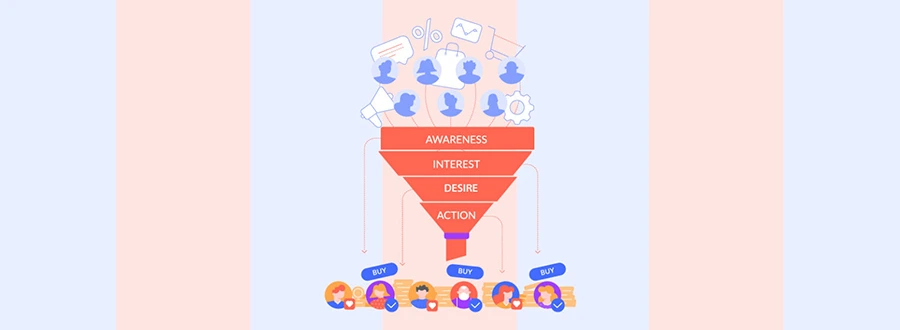
In general, there are four different stages in an e-commerce conversion funnel. Briefly, they are:
Awareness: Knowledge about your brand name and what you offer, say from a social media post or ad.
Interest: Engaging a potential customer through content that will sustain their interest
Desire: Creating a want for your product through ad strategies
Action: Customers’ buy’ the product.
These are the four stages of an e-commerce funnel. The awareness stage is where all the traffic enters the funnel, but as we know, this doesn’t mean they all will be interested in your product. And as the shape suggests, the number also reduces stage after stage. This means by the end of the funnel, only a small percentage of the leads will make the purchase.
Now let’s look in detail at these four stages and how to optimise them.
E-commerce funnel stages and how to optimise them
1. Awareness
The awareness stage is where the potential customer stumbles upon your brand. Presenting it as the solution to a problem or a goal makes sure that they can connect to it. Provide free content like blog posts that explain who you are, what you offer, and your niche. This way, the visitors will understand the benefits of your brand.
2. Interest
Once the customer is aware of your brand, engage them with content that will sustain their interest in you. This can be done by updating fresh content on your social media, blog, email newsletter, and YouTube. The content of these posts should sustain and heighten the interest in your product to lead them onto the next stage. Working on content SEO is critical at this stage; read more about content SEO.
3. Desire
After creating awareness and generating interest, it is time to create an urge in the leads for the product you have to sell. This desire to buy your product is what will lead a potential customer to your product pages and eventually into the cart. Employ specific strategies like CTAs to push the customer on to the next stage.
Read our blog on CTAs to understand more about the same.
4. Action
This stage is where the customer clicks the “Buy Now” button. However, this is also where the funnel tapers the most. To make the most of the numbers here, one has to create all the optimisations to prevent the customer from abandoning the purchase. Optimising your checkout page, adding secure payment portals, avoiding surprise shipping and other extra charges etc., can ensure that.
Best practices for building an optimised funnel
There is much to be done to build an optimised conversion funnel. Here’s a quick overview of how to do it.
- Identifying buyer journey using tools like Google Analytics
- Shaping the funnel stages and conversion triggers according to the type of business and action of your customers.
- Identifying the zone where a visitor converts to a lead and generating effective lead nurturing tactics.
After building an effective conversion funnel, it’s important to track Key Performance Indicators (KPI) like traffic, conversion rate, bounce rate, sales etc. Also, analyse the results using tools like user behaviour reports, recordings, and A/B test to choose the right optimisation. These will help you keep track of your leads’ changing behaviour and the efficiency of your funnel.
Now that you know how to use e-commerce funnels to boost your sales, get set to building an effective one for your business. Need us to do one for you? Contact us or drop an email to us at sales@computingaustralia.group.
Jargon Buster
Bounce rate – CMS is the software used to create and manage digital content.
Traffic – the number of visitors a website has.
A/B test – a user experience research methodology where two options are tested
KPI – Key Performance Indicators – a set of quantifiable measurements that demonstrates how efficiently a business is achieving its business targets.



