Boost Sales with
eCommerce Funnels
In the world of digital commerce, sales are the ultimate measure of business success. Every online store-large or small-relies on its ability to turn casual browsers into qualified leads and eventually into paying, loyal customers. But achieving this transformation doesn’t happen by accident. It requires a structured, strategic framework that guides shoppers through the decision-making process.
This is where ecommerce funnels, also known as conversion funnels, play a crucial role. They simplify the buyer’s journey, help you track customer behaviour at each stage, and highlight the exact optimisations needed to increase conversions. When implemented effectively, ecommerce funnels can significantly improve your sales and ROI.
This article-crafted by our SEO strategy team in Perth-explains what ecommerce funnels are, the stages within them, how to optimise each stage, and the best practices you should follow to generate more conversions consistently.
What Are Ecommerce Funnels?
An ecommerce funnel is a strategic model that illustrates the path a user takes from first discovering your brand to completing a purchase. While the details of the funnel may differ depending on your industry, product type, and customer behaviour, the core structure remains broadly similar across businesses.
Ecommerce funnels help you:
- Understand customer behaviour.
- Identify friction points causing drop-offs.
- Personalise marketing to increase conversions.
- Improve customer retention and lifetime value.
A well-built funnel works like a guided experience-addressing customer questions, handling objections, and offering the right nudge at the right time. Without a funnel, you risk losing leads due to confusion, poor user experience, or lack of trust-building interactions.
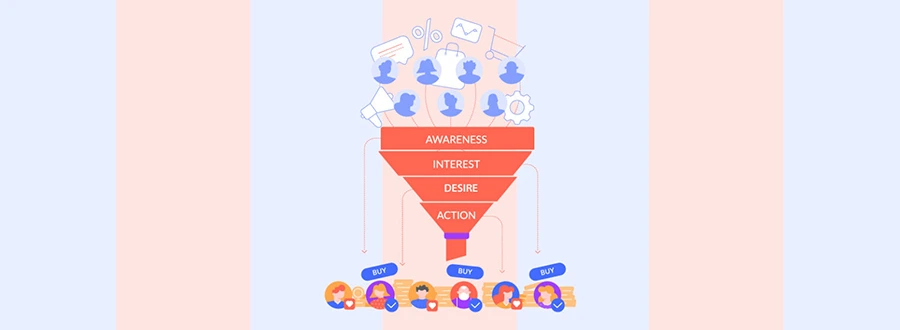
Most ecommerce funnels are split into four key stages:
1. Awareness – The customer discovers your brand.
2. Interest – They begin engaging with your content or products.
3. Desire – Their interest grows into a strong inclination to buy.
4. Action – The customer completes the purchase.
Let’s explore these stages in depth and learn how to optimise each one for maximum revenue.
Ecommerce Funnel Stages and How to Optimise Them
1. Awareness: Making Your Brand Discoverable
The awareness stage is the very top of the funnel (TOFU), where customers first learn about your existence. This might happen through:
- Social media posts or ads
- Google search results
- Influencer recommendations
- Blog content
- Word of mouth
- YouTube videos
- Podcasts or online communities
How to Optimise the Awareness Stage
A strong awareness strategy blends visibility with value. Here’s how to build one:
Create Informative, SEO-Optimised Content
Publish blog articles, guides, and videos that help your audience solve problems or answer questions related to your products.
Examples:
- “How to Choose the Best Running Shoes for Flat Feet”
- “The Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Home Décor”
This positions your brand as an authority.
Leverage Paid Ads
Run targeted Google Ads, Meta Ads, or TikTok ads to attract the right audience.
Build Social Media Visibility
Consistently post valuable content, reels, tutorials, and user-generated content.
Collaborate With Influencers
Micro-influencers in niche categories can introduce your brand to highly engaged communities.
Offer Valuable Lead Magnets
Provide:
- Free ebooks
- Product comparison charts
- Discount codes
- Style guides
- Free shipping campaigns
These incentives help users enter the funnel with interest already piqued.
2. Interest: Building Trust and Engagement
At this stage, prospects know who you are-but they need more information or assurance before considering buying from you. This is where mid-funnel (MOFU) nurturing becomes vital.
How to Optimise the Interest Stage
Publish Fresh, Consistent Content
Update your blog, social media feeds, and YouTube channel with content that answers questions like:
- How does this product work?
- What makes this product better than alternatives?
- What benefits will I get from using it?
Implement Email Marketing Sequences
Once a user subscribes, nurture them with:
- Welcome emails
- Product education
- Testimonials
- Special introductory offers
- Behind-the-scenes or brand stories
Use Retargeting Ads
People who visited your website but didn’t purchase should continue seeing your brand across platforms.
Retargeting boosts conversions significantly.
Share Social Proof
Displaying social proof increases trust and reduces hesitation.
Include:
- Customer reviews
- Testimonials
- Product ratings
- Case studies
- Before-and-after photos
Strengthen Content SEO
Optimise:
- Keywords
- Internal links
- Meta descriptions
- Page load time
- Image alt tags
This ensures customers can easily find relevant information.
3. Desire: Turning Interest into Strong Intent
This is the most critical stage. You’ve attracted the user, nurtured interest, and now must convince them to want your product.
How to Optimise the Desire Stage
Use Persuasive Product Pages
Your product pages must answer all questions before customers ask them.
Include:
- Clear descriptions
- High-quality images
- Videos or 360° views
- Feature-to-benefit storytelling
- Comparison charts
- FAQs
Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs)
Show what sets you apart:
- Free returns
- Eco-friendly packaging
- Lifetime warranty
- Price match guarantee
Implement Strong CTAs
Every page should direct users forward:
- “Add to Cart”
- “Buy Now”
- “Try it Risk-Free”
- “Claim Your Discount”
Use Psychological Triggers
- Scarcity: “Only 3 left in stock”
- Urgency: “Sale ends in 2 hours”
- Social proof: “500 people bought this today”
Add Bundles, Upsells, and Cross-Sells
Increase order value and conversions simultaneously.
4. Action: Completing the Purchase
This is where interested leads become paying customers. Unfortunately, it’s also the stage where most customers abandon the process.
How to Optimise the Action Stage
Streamline the Checkout Process
Common checkout issues include:
- Too many form fields
- Mandatory account creation
- Unexpected shipping costs
- Slow website speed
Solutions:
- Enable guest checkout
- Display total cost upfront
- Allow autofill
- Reduce clicks needed to complete a purchase
Add Trust Elements
- Secure payment icons
- SSL badges
- Clear return policy
- Customer service contact
Offer Multiple Payment Options
Consider adding:
- Credit/debit cards
- PayPal
- Google Pay
- Apple Pay
- Buy Now Pay Later (Afterpay, Klarna)
Reduce Cart Abandonment
Use:
- Exit-intent pop-ups
- Cart-recovery emails
- Retargeting ads
- Limited-time discount codes
Optimise Mobile Checkout
Since most ecommerce sales happen on mobile, ensure:
- Large CTA buttons
- Fast loading
- Easy navigation
- Clear text and layout
Best Practices for Building an Optimised Ecommerce Funnel
Creating a high-converting funnel involves more than understanding the stages. It requires continuous analysis, testing, and refinement.
Here are the top practices to follow:
1. Analyse the Buyer Journey Using Analytics Tools
Tools like Google Analytics, GA4, Hotjar, and Semrush help you understand:
- What channels bring most traffic
- Where users drop off
- How long customers stay on each page
- Which products attract most attention
- What actions users take before converting
With this data, you can refine the funnel to meet real customer behaviour.
2. Personalise Funnel Stages and Conversion Triggers
Not all customers behave the same way. Tailor your funnel for different segments:
- First-time visitors
- Returning customers
- High-intent visitors
- Discount-driven shoppers
- Loyal customers
Use personalised emails, recommendations, and messaging based on segment behaviour.
3. Identify Lead-Conversion Zones and Strengthen Lead Nurturing
Find the exact moment your visitors turn into leads. It could be:
- When they sign up for newsletters
- When they download a free guide
- When they add items to the cart
Then enhance these moments with:
- Better CTAs
- Seamless forms
- Attractive offers
- Retargeting sequences
4. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Some essential ecommerce KPIs include:
- Conversion rate
- Cart abandonment rate
- Traffic sources
- Average order value
- Bounce rate
- Customer lifetime value
- Cost per acquisition
Monitoring these metrics helps you assess whether your funnel is performing as expected.
5. Run Tests to Improve Funnel Efficiency
A/B testing allows you to experiment with:
- CTA styles
- Product page layouts
- Checkout flows
- Ad creatives
- Landing page content
- Email subject lines
Use behaviour analytics and recordings to identify friction points and test solutions.

After building an effective conversion funnel, it’s important to track Key Performance Indicators (KPI) like traffic, conversion rate, bounce rate, sales etc. Also, analyse the results using tools like user behaviour reports, recordings, and A/B test to choose the right optimisation. These will help you keep track of your leads’ changing behaviour and the efficiency of your funnel.
Now that you know how to use e-commerce funnels to boost your sales, get set to building an effective one for your business. Need us to do one for you? Contact us or drop an email to us at sales@computingaustralia.group.
Jargon Buster
Bounce rate – the percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page.
Traffic – the number of visitors a website has.
A/B test – a user experience research methodology where two options are tested
KPI – Key Performance Indicators – a set of quantifiable measurements that demonstrates how efficiently a business is achieving its business targets.

FAQ
What is an ecommerce funnel?
An ecommerce funnel is a strategic framework that maps out the stages a customer goes through before making a purchase-from first discovering your brand to completing the checkout. It helps businesses understand customer behaviour, optimise each stage, and improve conversions.
Why are ecommerce funnels important for online stores?
How can I increase customer interest once they know about my brand?
How often should I update my ecommerce funnel?
Funnel optimisation is an ongoing process. Review performance monthly and run A/B tests regularly to refine CTAs, page layouts, product images, and checkout flows.
Can ecommerce funnels improve customer retention?
Yes. Funnels don’t end at the purchase stage. Post-purchase flows-follow-up emails, loyalty programs, personalised recommendations, and excellent customer service-can turn first-time buyers into repeat customers.


