The Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity for Businesses
Internet is the lifeblood of the modern era. As the digital space becomes more advanced and integrates further into the day-to-day lives, safety concerns are also on the rise. With cybercrimes increasing daily, questions on the security of digital transactions are also growing. “Are my online communications safe? How can I pass sensitive information over the internet without the fear of misuse? Is my network safe? Are my customers’ data safe?” How you answer these questions depends on the strength of your organisation’s cybersecurity system. Cybersecurity acts as the armour that protects your personal and organisational data. So, what exactly is cybersecurity, and why should you care about it? What makes a sound cybersecurity strategy? Here’s a comprehensive cybersecurity guide to help you protect your and your customers’ data. But before that, let’s understand what a cyberattack is and the most common types of cyberattacks.
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyberattack is a deliberate and unauthorised attempt to collect, alter or erase sensitive data, typically with malicious intent. Hackers and cybercriminals are usually the perpetrators of cyberattacks. The majority of cyber-attacks are committed for ransom or stealing data, while a few are for fun, activism or state-sponsored. At times, users who are unaware of the significance of their actions might also become unsuspecting perpetrators. The most common example of this would be your device becoming a part of a botnet attack.
Types of Cyberattacks
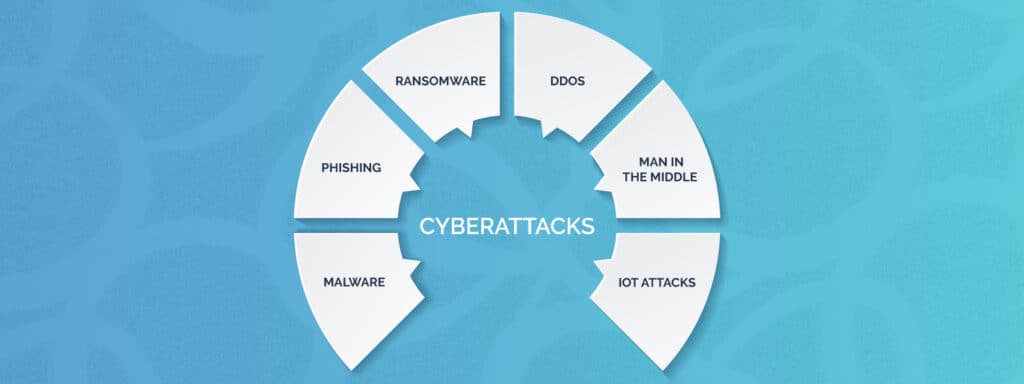
What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the combination of technologies, processes and everyday practices used for securing data, networks, and computer systems from cyberthreats. It is often used interchangeably with “information security” as it aims to safeguard digital information. But the two are actually different. Read our blog on Information Security vs Cybersecurity to know more. The protected data usually includes passwords, financial details, confidential business information, customer data, employee details and internal documents.
Cybercriminals aim to damage your organisation’s reputation at the expense of innocent customers who put their trust in you. Security breaches will enable attackers to collect data that they could manipulate to cause harm to your organisation as well as employees and customers. The prevention of security loopholes is thus essential for any business.
The 5 types of cybersecurity
To counter cyberattacks, you must adopt a strategic approach. There are five types of cybersecurity strategies to protect your organisation. They are:
- Critical infrastructure security: As the name suggests, this technique secures physical systems that contain critical infrastructure such as the electricity grid, traffic lights, hospitals, etc. Cyberattacks against such systems will affect regions or countries as a whole, which makes having contingency plans a must.
- Network security: Network security enables organisations to protect their computer networks from cyber threats. Machine learning technology is slowly being integrated into security plans to alert the authorities when unusual conditions, like abnormal traffic, is observed in a company network. Login options, passwords, firewalls, data encryption etc., help secure organisational networks.
- Cloud security: Cloud computing is becoming an inessential part of digital businesses, and most organisations are slowly adopting cloud infrastructure for an enhanced business experience. Cloud security refers to practices like user-defined routing configurations, web application firewalls, and AI-based threat detection that will create a fortress around your cloud environment to protect it.
- Internet of Things (IoT) security: IoT is regarded as the tool for the next technological revolution. With its wide variety of benefits, IoT can improve the way you work and live. Doing regular risk assessments is a critical step in mitigating cyber threats against IoT.
- Application security: Web applications are often vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Steps must start in the initial developing stages to ensure their security. Secure coding practices and antivirus programs are among the main constituents of application security.
Significance of cybersecurity
So why should you care about cybersecurity? You may have this question if you’ve never suffered a cyberattack. But it is estimated that 87% of organisations have experienced cyber-attacks at least once.
COVID-19 was not the only pandemic wreaking havoc across the world in 2020. Cybercrimes, too, were doing their own infestation, affecting hundreds of millions of cyberattacks every day. By the end of 2020, malware increased by 358%, while ransomware increased by 435%. These numbers speak for themselves.
SMBs are especially prone to cyberattacks. Because they have more valuable digital assets with lower security levels, SMBs are hackers’ favourite targets. Security breaches not only cause you monetary losses but the loss of trust of your consumers as well. Thus, investing in cybersecurity is a critical step in building the brand-consumer relationship. You can learn more about the significance of cybersecurity here.
Challenges for cybersecurity

While the cybersecurity field is constantly evolving, it is also continuously challenged. Cybercriminals are adopting practices to focus their attacks and selling their tools as commodities. This established cybercrime market makes it even harder to combat cyberattacks.
Challenges faced by cybersecurity include:
- Vulnerabilities to protective protocols of sensitive company data stored in cloud applications.
- Lack of cybersecurity awareness in end-users leads to users unknowingly allowing malware to infect their systems and networks.
- Shortage of trained cybersecurity professionals.
How to identify a cyberattack
Rapid threat detection is key to combating cyberattacks. The following signs could denote a cyberattack:
- Abnormal spikes in site traffic
- Computer processing slows down
- Storage space is suddenly full
- There are applications in your system that you didn’t install
- Programs open and close randomly
- Security software gets disabled
- Popups appear frequently
- You get locked out of your system
- Passwords get reset without your knowledge
Best cybersecurity practices to protect yourself
All businesses should invest in defensive cybersecurity solutions to prevent cyberattacks and their consequences. Employees should also be instructed on safe cybersecurity practices. The following are some effective options to safeguard your network and computers.
- Install antivirus software: Antivirus is like a vaccine shot for digital viruses. It is an effective preventative measure that will help detect threats and remove them. Antivirus software will also alert you about potentially harmful web pages and software. A good portion of computer systems has in-built antivirus software. However, we suggest installing a reputed antivirus package for comprehensive protection. To learn about antivirus software and how to choose the right one, read our blog.
- Use firewalls: Firewalls act as digital walls that filter out suspicious network traffic. It will assess the safety of every packet of data sent to your computer and will only allow legitimate entities to enter the system. Both software and hardware-based firewalls are available to choose from.
- SSO: Single sign-on is an authentication service that allows you to access an entire platform of accounts and software using one username and password. For example, when you sign up for a Google account, you’re able to access Gmail, Google Docs, Google Drive, YouTube, and other Google products using that account. Enabling SSO for employees in corporations will help keep the intruders out.
- Implement MFA: Multi-factor authentication is a login process that requires more than a username and password to get access. Since users need to confirm their identity via more than one verification process, it is more secure than single-factor authentication. MFA methods usually include:
-Code sent to email/phone/application
-Automated phone call
-PIN
-Security question
- Use VPNs: Virtual private networks (VPNs) encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data online. They allow users to browse on the internet without being spied on. Some corporations use password-protected VPN access, which is another added layer of protection for your identity. While VPN is effective against spyware, it can’t stop viruses from entering your systems.
- Download and update patches: Even though software vendors regularly release bug fixes and security patches, people tend to ignore them. Downloading and updating your software to the latest version will make it harder to hack into. The latest release will always be more protected than the previous versions. If you tend to be forgetful, there are options available to update software automatically.
- Unique passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for each application. It’s advisable to make passwords longer than 8 characters and mix letters, numbers, and symbols. Ensure that you don’t use the same passwords for multiple accounts – one password compromised will lead to all accounts being vulnerable. Also, avoid saving your passwords on the system.
- Monitor financial details: Though it might be hard to follow through, try to review your credit card reports and financial statements regularly. Do not give your bank account details to anyone unless you are sure that the person on the other end is authentic. Try not to save payment details on every website.
- Backup data: Backing up data allows you to regain your data easily even if your system undergoes a cyberattack. You can back up on the cloud using applications like OneDrive as well as on a hard drive location.
- Report: If you receive any suspicious emails or observe any unusual activities on your workplace networks, always report to the authorities as soon as possible. Employers should make it easy for employees to escalate such issues to detect threats and avoid huge damages.
Want to learn more about good cybersecurity practices? You can do so by following this link.
Protecting your business with Disaster Recovery Strategies
The above steps can be useful as a first line of defence against cyberattacks. But for an organisation, this will definitely not be enough. Despite being vigilant, your organisational cybersecurity can be breached at times.
A cyber breach causes a huge downtime, financial loss, loss of credibility in the industry, and loss of trust amongst your customers. It is important to note that many SMBs never recover from a cyberattack – they end up shutting the shop. It is therefore imperative that your business has a robust Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) in place. A DRP will help you to prevent cyberattacks in the first place and get your business to recover and functional fast if you do become a cybercrime victim. Read our blog on Disaster Recovery to know more
Cyberattacks are intimidating and for genuine reasons. They cause millions of losses around the globe and can even push a business into a fatal pit from which they can’t climb out. However, with awareness and good cybersecurity practices, you’ll be able to prevent and handle such issues easily. This guide on cybersecurity has touched on the major points, but don’t hesitate to reach out to our team if you need more information. You can contact us or emails us at cybersecurity@computingaustralia.group. Our group of experienced professionals will be available 24/7 to help you with your cybersecurity troubles.
Jargon Buster
Data breach: When a hacker gains access to an organisation’s or individual’s data through malicious ways, it’s referred to as a data breach.
Authentication: A verification process that proves your identity is called the authentication method.
Botnets: Botnets are collections of malware-infected computers used to carry out cyberattacks.
Keylogger: It is software that monitors a system’s activity and gives hackers access to personal information.
Spyware: a spying software that observes a user’s online activities and steals personal information.
Revised on 24/03/2022
Added section on Disaster Recovery, infographics
Updated Cybersecurity and Cyberattack sections and reordered sections.

